Please click here to access the main AHDB website and other sectors.
- Home
- Knowledge library
- Identification and management of nematodes in field crops
Identification and management of nematodes in field crops
A diverse group of slender worms, most nematode (Nematoda) species are parasitic – feeding on plants, bacterial, fungi or other nematodes. Also called roundworms or eelworms, discover which harm crops and which support a healthy soil ecosystem.
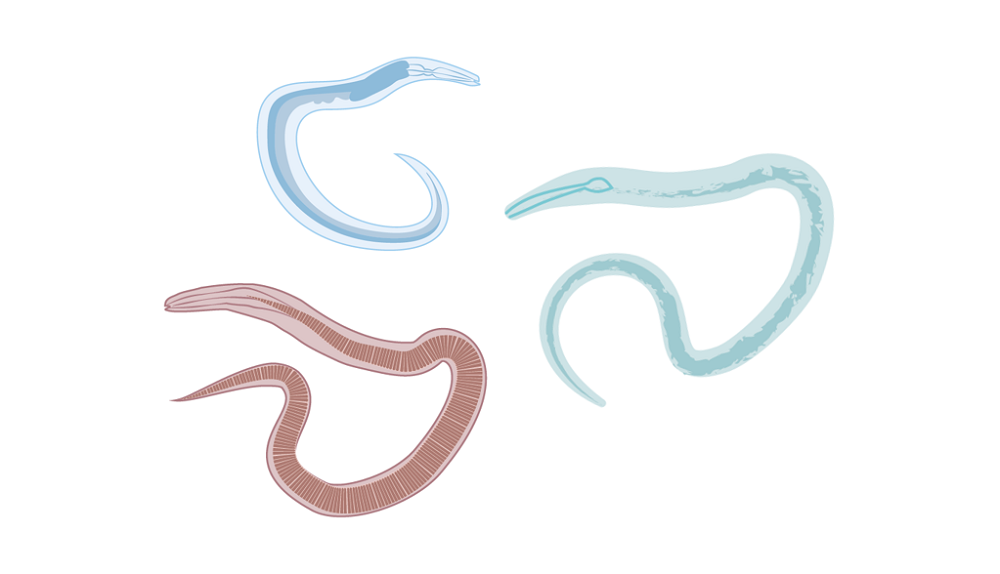
Defining features of nematodes
Soil nematodes are microscopic – less than 3 mm long and only 15–100 µm wide. Although difficult to distinguish, they can be identified by their mouthparts. They are grouped according to their feeding habits:
- Bacterial feeders
- Fungal feeders
- Omnivores
- Predators
- Plant feeders (parasites)
Plant-parasitic nematodes
Plant-parasitic nematodes will always be present in agricultural soils, but many are not serious pests. Find about the plant-parasitic nematodes of most concern in UK agriculture.
How to encourage natural enemies of field crop pests
Several nematode species help control other pests.
 Jon Oakley.JPG)


 BBRO.JPG?v=637828037620000000)
 Bayer CropScience.JPG?v=637828037620000000)

 Rothamsted Research.JPG?v=637828037630000000)